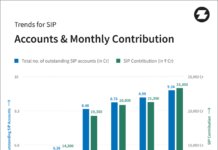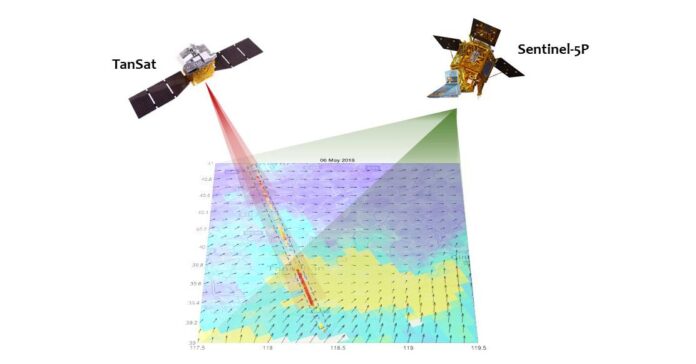
A coordinate measurement on anthropogenic CO2 emission from TanSat (China) and Sentinel-5P (Europe)
Chinese and European satellite tv for pc missions to advance international carbon dioxide monitoring
BEIJING, CHINA, October 25, 2022 /EINPresswire.com/ — An worldwide analysis staff has analyzed measurements from the TanSat mission and the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor mission to determine carbon dioxide from human actions. This is the first attempt to use TanSat measurements to detect anthropogenic, or human-caused, carbon dioxide emission signatures. Quantifying anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions is one of the crucial necessary necessities wanted for greenhouse gases to be monitored on a world foundation.
The staff, with researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Finnish Meteorological Institute, printed their analysis within the journal Advances in Atmospheric Sciences on October 25.
Carbon dioxide is acknowledged as crucial anthropogenic greenhouse fuel due to its vital impression on international warming and local weather change. Because of this, quite a lot of satellite tv for pc missions devoted to atmospheric greenhouse measurements have been developed within the final decade.
At the United Nations Climate Change Conference held in Paris in 2015, contributors agreed to scale back greenhouse fuel emissions to forestall international floor temperature will increase. Slowing down international warming represents a problem confronted by the worldwide inhabitants within the twenty first century. Concentrations of carbon dioxide proceed to rise due to anthropogenic actions resembling fossil gasoline combustion and land-use change. The emissions associated to the combustion of fossil fuels are notably localized, with city areas being the dominant contributor liable for greater than 70% of world emissions. Yet it has been particularly difficult for scientists to acquire the excessive precision measurements they wanted to examine anthropogenic emissions from cities.
TanSat, launched in 2016, is China’s first international carbon dioxide monitoring satellite tv for pc. Tan is Chinese pronunciation of carbon. While TanSat has been offering researchers with information for a number of years, new algorithms have been just lately added to the TanSat devices that tremendously improved TanSat’s measurement precision.
The staff carried out their examine two units of measurements collected over two cities. The staff used TanSat carbon dioxide information captured in May 2018 close to Tangshan, China, and in March 2018 close to Tokyo, Japan. They in contrast the TanSat information to nitrogen dioxide measurements captured by the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument onboard the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite tv for pc on the identical dates over the identical cities.
“We analyzed TanSat data in synergy with European Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor TROPOMI nitrogen dioxide observations to help the detection of anthropogenic plumes and to analyze the carbon dioxide-to-nitrogen dioxide ratio,” mentioned Dongxu Yang, from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Their two case research present TanSat carbon dioxide measurements have the potential to seize the anthropogenic variations within the plume and have spatial patterns like that of the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument’s nitrogen dioxide observations. In addition, the carbon dioxide-to-nitrogen dioxide ratio in Tangshan, China, and Tokyo, Japan, align with the emission inventories.
“This is an important step in TanSat data analysis. The next step is to infer emissions and to prepare for the TanSat-2 constellation including the joint analysis of CO2 and NO2 plumes,” mentioned Janne Hakkarainen, from the Finnish Meteorological Institute.
Looking forward, the staff has plans to increase this analysis. “The TanSat is our first attempt on global carbon monitoring. The next generation of China’s Global Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Satellite mission, TanSat-2, is now in the design phase,” mentioned Yi Liu, from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
According to Liu, TanSat-2’s goal measurements will deal with cities with an 800–1000 kilometer large swath to report the gradient of carbon dioxide from metropolis central to rural areas utilizing an imaging course of and a 500 meter footprint measurement to enhance the emission estimation accuracy. TanSat-2 shall be a constellation of satellites distributed into a minimum of two orbits within the morning and afternoon to cowl a metropolis or a degree supply twice a day.
“Our goal is to use satellite measurements to improve our knowledge on carbon cycle and to further analyze and constraint the carbon dioxide sources and sinks and their uncertainties,” mentioned Liu.
The analysis staff consists of Dongxu Yang, Yi Liu, Zhaonan Cai, from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics on the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Janne Hakkarainen, Iolanda Ialongo, and Johanna Tamminen, from the Finnish Meteorological Institute.
This analysis is funded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Academy of Finland.
Jenny Lin
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences
08299505310
e-mail us right here
Visit us on social media:
Facebook
Twitter
![]()