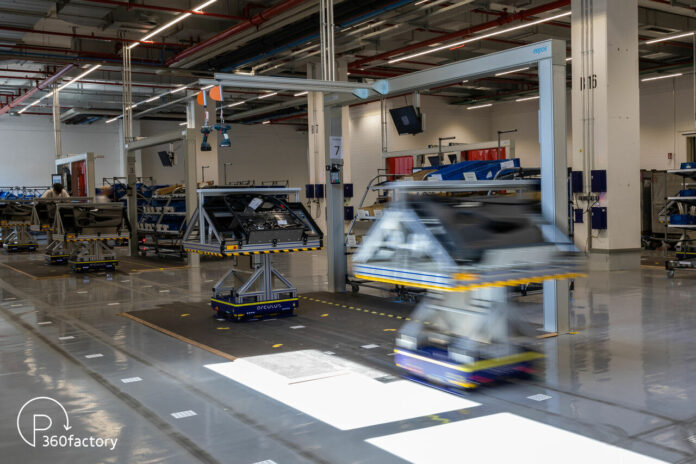
Growing complexity in merchandise and demand are altering the necessities for production. It has to adapt with ever better flexibility to particular buyer wants, short-term market modifications, and sustainability points. It is more and more tough to map a traditional conveyor belt assembly onto this complexity. That means of doing issues is based mostly on a precept of uniform cycle time for every product at each office in a set sequence. By distinction, modular assembly works and not using a belt or a uniform tempo of labor.
In lieu of a inflexible conveyor belt, dynamic procedures shift with a variable sequence of stations and variant-dependent processing occasions (digital conveyor belt). In preparation for subsequent collection software, Project Manager Wolfgang Kern’s workforce in Audi’s Production Lab is implementing that concept in inside door panel pre-assembly on the Ingolstadt plant. “Modular assembly is one of our answers to future demands on production,” says Gerd Walker, Member of the Audi Board of Management for Production and Logistics. “We’re using digital technology purposefully for the benefit of our employees, while achieving more flexible and efficient assembly,” Walker provides. “At the same time, this project is a prime example of our open innovation culture, where we are developing networked production in agile teams.” In the pilot venture, consultants are confirming feasibility, on one hand, and modular assembly’s potential, on the opposite, whereas concurrently forging further experience.
One main benefit of the versatile system is that Audi can make use of individuals who can not work on the road due to bodily limitations. “We are able to adapt the working environment to their conditions, which is currently only possible to a very limited extent at the conveyor belt,” says Kern. “We’re using more flexible automation in the production process in order to take the burden off people.” Thanks to the variant-dependent processing time as an alternative of a uniform cycle all staff profit from a lighter workload. This permits for ergonomic adaptation to particular person wants.
Guidance Logic Ensures Flexibility
In take a look at operation, duties not comply with a uniform sequence. Instead, they’re structured to meet explicit wants. Automated guided automobiles (AGVs) carry door panels proper to the station the place the elements want to be assembled. For instance, gentle packages are put in with cables and lighting parts at one station. Accordingly, jobs that don’t have a light-weight package deal bypass that station. At one other station, a employee assembles all the solar blind that is obtainable for the rear doorways as an choice. Because of its predefined tempo, on the conveyor belt this process would have to be divided up between two or three employees, which is inefficient and can jeopardize high quality. If jobs are piling up at one station, the AGVs drive the product to the subsequent required station with the least attainable quantity of ready time. In addition, the configuration of the workspaces is cyclically checked and adjusted. “Compared with the way things are organized today, the flexibility with the underlying guidance logic is an essential advancement,” Kern emphasizes. Unlike a conveyor belt, the person stations and modular production system are usually not designed for secure demand (optimum working level). Instead, they will be operated effectively inside a specific spectrum (optimum working vary).
Logistics and Quality Processes Can Be Efficiently Integrated
Where element variability is excessive, the goods-to-person precept is the answer. For occasion, AGVs carry the appropriate sorts of cable harnesses for door panels to employees who then take the elements they want. The different similar elements return to the stand-by place, as a result of normally a unique element variant will be wanted for the subsequent door panel. Providing sorted elements through AGVs makes upstream separation redundant. The automobiles are localized down to the centimeter through a radio community. A central laptop guides the AGVs. In addition, digital camera inspection also can be built-in into the standard course of. Irregularities can be managed extra rapidly and simply this fashion than on a conveyor belt. This helps keep away from unexpected further labor. “We’re combining the conveyor belt’s high degree of division of labor with a holistic eye toward lean principles and the new possibilities that cyber-physical production systems offer,” Kern explains.
Productivity Increase of About 20 Percent
The collection pilot is producing priceless insights and permitting engineers to derive serial functions. “By reducing production time through an orientation toward value creation and self-steering, we are able to increase productivity by about 20 percent,” Kern says. The subsequent step for Project Manager Kern and his workforce is to combine modular assembly at a bigger scale into pre-assembly. That is the place we discover excessive variability and dynamics that may be dealt with extra effectively than is at present attainable. “De-linking the stations makes it possible to reschedule things without much effort,” says Kern. Thanks to the versatile {hardware} and automated guided automobiles, it is typically the case that solely the software program wants to be adjusted. Stations can be tailored to merchandise and demand extra simply than on an interlinked conveyor belt.