As depletable assets, metallic uncooked supplies are wanted for a lot of future applied sciences, together with electromobility. The high-tech metals indium and germanium, cobalt, lithium, and uncommon earths are on the 2020 list of critical raw materials for the EU. This checklist of economically essential uncooked supplies with a excessive provide danger is meant to assist in the negotiation of commerce agreements in addition to drive analysis, innovation, and sustainable procurement.
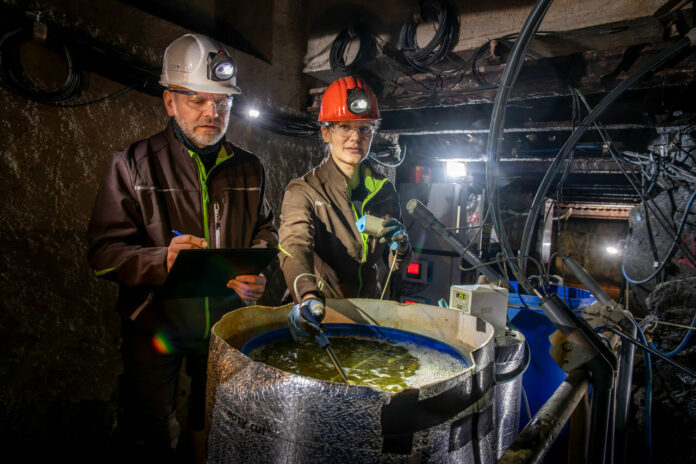
Many major uncooked supplies are present in just a few nations worldwide. Their geographic distribution is uneven, and they’re troublesome to entry. In some circumstances, they happen in such small portions that extraction is unprofitable. Moreover, mining actions have a drastic affect on the setting. Reason sufficient for the Audi Environmental Foundation, along with the Institute of Thermal, Environmental and Resources’ Process Engineering on the Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, to determine different extraction strategies for securing uncooked supplies. The two-year analysis challenge addressed the query of learn how to make mining extra sustainable. To this finish, the researchers put idea into apply each within the laboratory and underground in actual working environments in a analysis mine.
Combination of strategies for sustainable extraction of high-tech parts
The intention is to extract high-tech parts from ores with out destroying the pure setting by means of large-scale drilling and blasting. In distinction to traditional ore mining, microinvasive strategies much like trendy surgical practices are used right here. This has a number of benefits: No heavy equipment, a lot much less power, and fewer chemical compounds are used, and there’s additionally no harm to the panorama. “The process is environmentally friendly and innovative, as major mining activities are largely avoided and even small quantities of ore can be extracted,” says Rüdiger Recknagel, Director of the Audi Environmental Foundation. According to Recknagel, this strengthens import independence, thus rising provide safety.
The course of, often known as in-situ bioleaching, was developed and optimized within the laboratory earlier than lastly being examined below actual circumstances within the analysis mine on the Freiberg University of Mining and Technology. It works by having researchers drill small holes within the ore vein underground. Through leaching, the dear parts are dissolved from the ore with the assistance of microorganisms which might be already current within the mine. “The bacteria are little miners that help transfer the metal ions to a solution,” explains Roland Haseneder of the Institute of Institute of Thermal, Environmental and Resources’ Process Engineering Through this course of, some of the mineral elements dissolve. The specialists mix this step with direct two-stage membrane remedy. “Working on site means there are no transport costs or logistics efforts,” says Haseneder. Additionally, the plant separates the microorganisms and returns them to the leaching course of within the spirit of a round economy.
The intention of this course of is to separate and enrich indium and germanium from a multicomponent combination. These two strategic metals are mandatory for an array of high-tech merchandise reminiscent of flat screens, contact screens, navigation programs, fiber optic expertise, laptop chips, photovoltaic programs, and automotive bearings.
Underground laboratory and discipline exams show effectivity
The specialists wished to learn how the system would carry out at a depth of 147 meters below circumstances with over 90 p.c humidity and dripping acidic water at ten levels Celsius. Important parameters included the composition of the bacterial resolution, enrichment with goal parts, the method parameters used, and the yield of goal parts. The exams proved the effectivity of the system. “We adjusted the pressure, flow rate, and purification processes to significantly improve separation,” Haseneder says. Haseneder additionally says the separation effectivity for germanium was elevated by 20 p.c in comparison with the laboratory experiments.
In the longer term, this sustainable extraction course of will even be used for different parts reminiscent of cobalt in different deposits. The course of is particularly appropriate for the extraction of worthwhile parts each from low-grade ores with a low focus of worthwhile supplies and from secondary uncooked supplies effectively as to be used at current mining websites utilizing the infrastructure that’s already in place. Haseneder additionally suggests the method might discover utility in different fields reminiscent of city mining. At the Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, the seek for appropriate companions for utility at different websites is in full swing. The final imaginative and prescient is to implement microinvasive mining globally.
About the Audi Environmental Foundation
The Audi Environmental Foundation is an lively supporter of analysis into new applied sciences and scientific strategies for a livable future. Its said mission is to assist defend the setting and to create and promote methods to behave sustainably. The basis significantly focuses on advancing and growing environmentally pleasant applied sciences, environmental education schemes, and efforts to guard the pure foundations of human, animal, and vegetation. It was based in 2009 by AUDI AG as an entirely owned subsidiary and is a component of the corporate’s work in help of social and environmental causes.